How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, bridging the gap between technological advancement and recreational/professional pursuits. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental regulations and components to mastering flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to troubleshooting common issues and exploring advanced maneuvers, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for both novice and experienced pilots.
Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to capture breathtaking landscapes or a professional seeking to utilize drones for commercial applications, mastering the art of drone operation requires a solid foundation in safety, technical knowledge, and practical skills. This guide provides that foundation, equipping you with the necessary knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Drone Regulations and Safety

Safe and legal drone operation requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety protocols. This section details FAA regulations, pre-flight checklists, registration procedures, and a comparison of drone certifications.
FAA Regulations for Drone Operation
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States governs drone operation. Airspace is categorized into classes (A through G), each with specific regulations. Class G airspace, typically found at lower altitudes and away from airports, has the least restrictions. Higher classes, closer to airports and with heavier air traffic, have stricter rules, often requiring prior authorization for drone flights.
Unauthorized flights in restricted airspace can result in penalties.
Pre-Flight Checklist for Safe Drone Operation, How to operate a drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe operation. This includes verifying weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), checking airspace restrictions using apps like B4UFLY, ensuring the drone’s battery is adequately charged, and conducting a physical inspection of the drone for any damage.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, you can refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible drone piloting ensures both your safety and the safety of others.
Registering a Drone with the FAA
Most drones require registration with the FAA. The process typically involves creating an account on the FAA’s DroneZone website, providing drone information, and paying a registration fee. This ensures accountability and helps track drone operations.
Drone Certifications and Requirements
Different drone certifications exist, catering to various levels of operation and expertise. The requirements vary, including flight experience, knowledge tests, and specific operational limitations.
| Certification Level | Requirements | Flight Restrictions | Operational Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recreational | Registration with FAA (if applicable) | Limited to visual line of sight (VLOS), no commercial use | Basic flight operations |
| Part 107 (Commercial) | Written exam, background check | VLOS or beyond, with appropriate authorizations | More complex operations, commercial use permitted |
| Advanced Certifications | Vary depending on the specific certification | Often includes waivers for certain airspace restrictions | Specialized operations (e.g., night flights, BVLOS) |
Drone Components and Functionality
Understanding the individual components and their functions is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section describes the major components of a typical drone, different camera types, control methods, and maintenance procedures.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is learning about pre-flight checks and procedures, which are essential for safe and effective operation. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone to ensure you’re fully prepared before your first flight.
Mastering these fundamentals will significantly improve your drone piloting skills and allow you to explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography responsibly.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components: propellers (for propulsion), motors (for spinning the propellers), a battery (for power), a flight controller (for managing flight parameters), and a camera (for capturing images and videos). Each component plays a vital role in the drone’s overall functionality.
Types of Drone Cameras and Capabilities
Drone cameras range from basic HD cameras to high-resolution cameras with advanced features like 4K video recording, image stabilization, and various lenses. The choice of camera depends on the specific application and desired image quality.
Drone Control Methods
Drones can be controlled using joysticks (providing more precise control) or app-based control (offering user-friendly interfaces). App-based control is often easier for beginners, while joystick control offers greater precision for experienced pilots.
Drone Component Maintenance
- Regularly inspect propellers for damage.
- Clean the drone’s body and components.
- Carefully store and charge the battery.
- Perform firmware updates as needed.
- Calibrate the compass and sensors periodically.
Pre-Flight Procedures and Checks
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight procedure is necessary. This includes calibrating the drone’s sensors, inspecting the physical components, verifying battery levels, and planning the flight path.
Calibrating the Drone’s Compass and Sensors
Calibrating the compass and other sensors ensures accurate flight data and prevents unexpected behavior. The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
Pre-Flight Inspection of Drone Components
A visual inspection of the propellers, motors, body, and other components helps identify any damage or loose parts before flight. This preventative measure can prevent accidents and malfunctions.
Confirming Battery Levels and Flight Time Estimations
Before flight, it’s crucial to verify that the battery is adequately charged and to estimate the flight time based on the battery’s capacity and the drone’s power consumption. Always have a spare battery available.
Planning a Flight Path
Planning the flight path involves identifying potential obstacles (trees, buildings, power lines), considering wind conditions, and ensuring the drone remains within legal and safe operational boundaries. Using flight planning software can aid in this process.
Operating the Drone: Takeoff, Flight, and Landing

Safe and controlled drone operation requires proper techniques for takeoff, flight maneuvers, emergency procedures, and landing. This section details these procedures.
Safe and Controlled Takeoff
A safe takeoff involves a slow and steady ascent, ensuring the drone maintains stability and avoids obstacles. Always check the surrounding environment before initiating takeoff.
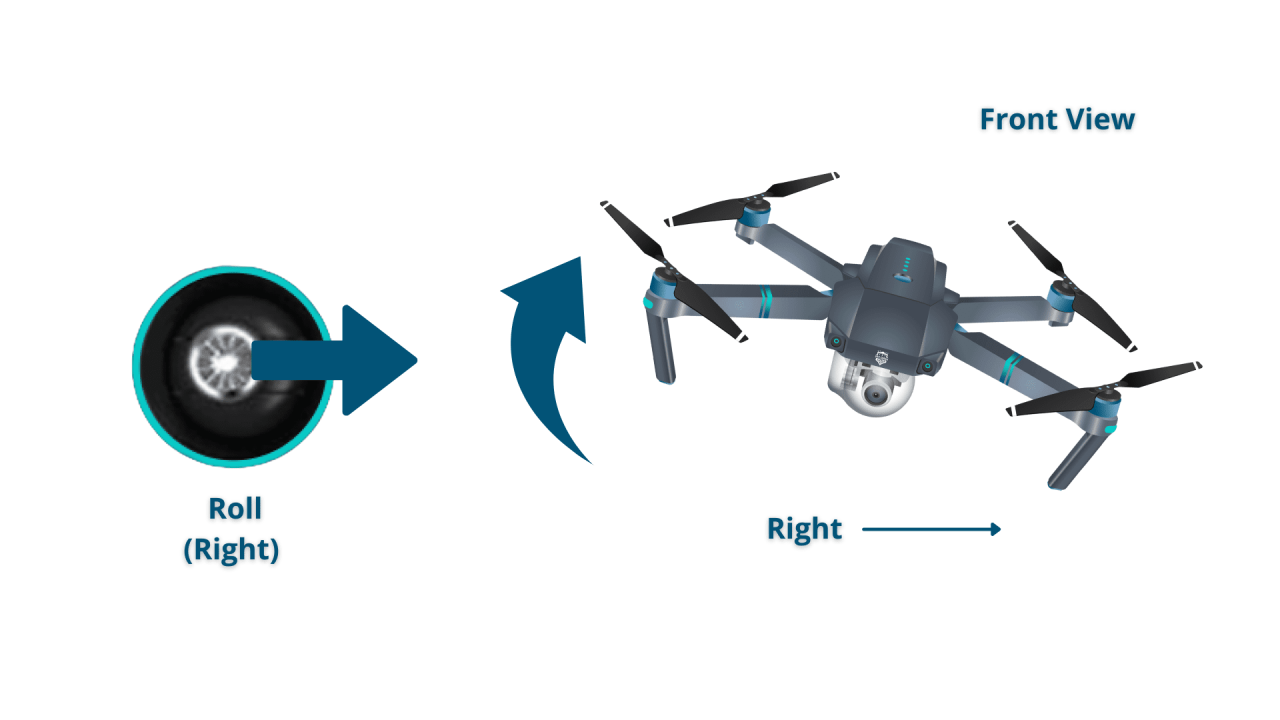
Maneuvering the Drone
Maneuvering involves controlling the drone’s movement in various directions (forward, backward, left, right, up, down) and adjusting its altitude. Smooth and controlled movements are key to preventing accidents.
Emergency Maneuvers and Failsafes
Understanding emergency maneuvers and failsafes is crucial. This includes knowing how to return the drone to its home point, how to initiate an emergency landing, and how to react to unexpected situations (e.g., loss of signal).
Smooth and Controlled Landing
A smooth landing involves a slow and steady descent, ensuring the drone touches down gently and avoids damage. Always check the landing area for any obstacles before initiating landing.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, stabilization techniques, composition principles, and post-processing methods.
Settings for High-Quality Aerial Media
Optimizing camera settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, is crucial for capturing sharp and well-exposed images and videos. Experimentation and understanding the relationship between these settings are essential.
Achieving Stable Shots
Stable shots are vital for professional-looking results. Techniques like using image stabilization features, flying smoothly, and avoiding sudden movements help achieve this.
Composing Visually Appealing Aerial Shots
Composition is key to creating visually appealing shots. Using the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques can significantly enhance the aesthetic quality of aerial footage.
Post-Processing Techniques
Post-processing software allows for enhancing drone footage. Techniques like color grading, sharpening, and noise reduction can significantly improve the final product.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section provides solutions for common drone malfunctions and offers a troubleshooting guide.
Solutions for Common Drone Malfunctions
Common issues include low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, and motor failures. Addressing these issues promptly and correctly is crucial for preventing further damage.
Recovering a Crashed or Malfunctioning Drone
If a drone crashes or malfunctions, carefully assess the situation, identify the cause of the problem, and follow the appropriate recovery procedures. Safety should always be the top priority.
Interpreting Error Messages
Understanding error messages displayed on the drone’s controller or app helps in diagnosing and resolving problems quickly. Refer to the drone’s manual for detailed explanations of error codes.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Low Battery Warning: Land immediately and replace with a fully charged battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor and propellers for damage. If necessary, replace the faulty component.
- Drone unresponsive: Check battery levels, signal strength and reboot the drone and controller.
Drone Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation methods extend the lifespan of a drone and its accessories. This section details best practices for both.
Best Practices for Drone Storage
Store the drone in a clean, dry, and safe location away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Use a protective case to shield it from damage.
Safely Transporting a Drone
When transporting a drone, use a protective case or bag to prevent damage during transit. Securely fasten all components to prevent them from shifting during transport.
Transporting in Various Climates
Take extra precautions when transporting a drone in extreme climates. Protect it from extreme heat, cold, moisture, and sudden temperature changes.
Essential Considerations for Long-Term Drone Storage
Store the drone in a climate-controlled environment, ideally with low humidity. Regularly check the battery charge level and condition. Consider using desiccant packs to absorb moisture.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced techniques for experienced drone pilots, including waypoint navigation, automated flight planning, and advanced maneuvers.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Planning
Waypoint navigation involves pre-programming a flight path using waypoints, allowing for autonomous flight. Automated flight planning software can simplify this process.
Advanced Drone Features
Features like follow-me mode (the drone automatically follows a designated subject) and obstacle avoidance enhance flight safety and capabilities.
Performing Drone Flips and Other Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like flips and rolls require practice and skill. Start with simpler maneuvers and gradually progress to more complex ones.
Illustrative Example of a Complex Maneuver
Imagine a drone performing a complex aerial maneuver: it ascends rapidly, then executes a 360-degree barrel roll while maintaining a stable camera angle, capturing a sweeping panoramic view before smoothly descending to a pre-determined landing point. The camera angle remains consistent throughout the maneuver, providing a seamless and dynamic visual experience.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. From navigating complex regulations and understanding your drone’s mechanics to mastering flight techniques and troubleshooting potential problems, this guide has provided a roadmap to safe and proficient drone operation. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for responsible drone piloting, allowing you to explore the limitless possibilities of aerial technology responsibly and effectively.
Safe flying!
Questions Often Asked
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery size, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes per battery.
How do I know if my drone’s battery is fully charged?
Check the battery indicator lights on the drone or in your controller app. A full charge is usually indicated by solid lights or a 100% display.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
Immediately initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available. If not, carefully maneuver the drone back to your location using visual cues.
Can I fly my drone in the rain?
No, most consumer drones are not waterproof and should never be flown in rain or other wet conditions. This can cause irreparable damage.
